HAAKE, Steve, JOHNSON, Thomas W., BOURNE, Jessica, QUIRK, Helen and BULLAS, Alice (2023). Parkrun as self-managed cardiac rehabilitation: secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey of parkrun in the UK. Open Heart, 10 (2).
|
PDF
openhrt-2023-002355.pdf - Published Version Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
|
PDF (Data supplement 1)
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(Supp1).pdf - Supplemental Material Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (107kB) | Preview |
|
|
PDF (Data supplement 2)
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(Supp2).pdf - Supplemental Material Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (97kB) | Preview |
|
|
PDF
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(AM).pdf - Accepted Version Creative Commons Attribution. Download (366kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](/32210/21.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed%28AM-figure1%29.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG)
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(AM-figure1).jpg - Accepted Version Creative Commons Attribution. Download (378kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](/32210/23.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed%28AM-figure2%29.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG)
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(AM-figure2).jpg - Accepted Version Creative Commons Attribution. Download (522kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](/32210/22.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed%28AM-figure3%29.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG)
Haake-ParkrunAsSelf-managed(AM-figure3).jpg - Accepted Version Creative Commons Attribution. Download (616kB) | Preview |
Abstract
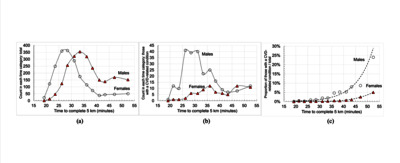
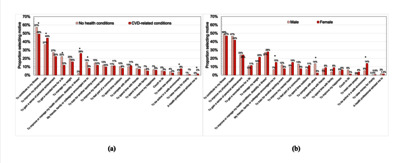
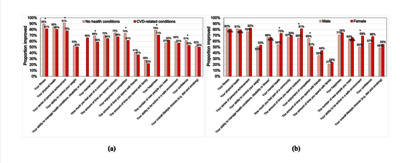
Objectives: Cardiac rehabilitation following a cardiovascular disease (CVD)-related illness has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attack and hospital admission. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends 3–5 days per week of moderate to vigorous exercise. Despite this, only 38% of those eligible complete rehabilitation programmes. Parkrun organises free, weekly, timed, 5 km running or walking events. The aim of this study was to investigate whether parkrun can support self-managed cardiac rehabilitation. Methods: We undertook a secondary analysis of a survey of UK parkrunners, comparing responses of those reporting no health conditions (n=53 967) with those with one or more CVD-related conditions (n=404). Thematic analysis was used to analyse 53 open-ended text comments from the latter. Results: Four hundred and four respondents (0.7% of the total) reported CVD-related conditions with the largest proportions among those walking the event (24% of male participants and 5% of female participants). For those doing <3 days per week of physical activity at registration, 47% increased activity to ≥3 days per week. Among those with CVD-related conditions, participation in parkrun led to perceived improvements in fitness (81% of participants), physical health (80% or participants) and happiness (74% of participants). Two thirds reported improvements to their ability to manage their condition(s) and half to their lifestyle choices. Analysis of 53 open-text comments revealed that those with CVD-related conditions used parkrun to monitor their condition and were motivated by encouragement from the parkrun community. Enjoyment and fun were important for engagement, although some individuals were dispirited by poor performance due to their conditions. Conclusions: Individuals with CVD-related conditions used parkrun to self-manage their rehabilitation; this applied to those attending parkrun following disease onset as well as those engaged with parkrun prior to their condition. Parkrun, or events with similar characteristics, could support self-managed cardiac rehabilitation.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Additional Information: | ** Embargo end date: 26-07-2023 ** From BMJ via Jisc Publications Router ** Licence for this article starting on 26-07-2023: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ** Peer reviewed: TRUE ** Acknowledgements: We would like to thank Chrissie Wellington and Mike Graney at parkrun for their support in this research and to Tim Chico and Rachel Drew for their helpful suggestions on the manuscript. We would also like to thank all participants who took the time to fill out our survey. **Journal IDs: eissn 2053-3624 **Article IDs: publisher-id: openhrt-2023-002355 **History: published_online 26-07-2023; accepted 06-07-2023; published 07-2023; submitted 28-04-2023 |
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | epidemiology, cardiac rehabilitation, coronary artery disease, delivery of health care |
| Identification Number: | https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2023-002355 |
| SWORD Depositor: | Colin Knott |
| Depositing User: | Colin Knott |
| Date Deposited: | 01 Aug 2023 15:54 |
| Last Modified: | 11 Oct 2023 13:00 |
| URI: | https://shura.shu.ac.uk/id/eprint/32210 |
Actions (login required)
 |
View Item |
Downloads
Downloads per month over past year

 Tools
Tools Tools
Tools